
What is Robotic Process Automation RPA & its Key Benefits?
Furthermore, many of these algorithms and focused solutions are being embedded into new versions of existing enterprise systems. This means your decision to choose one technology over another today can hinge on variables other than the algorithm’s or solution’s ability to do its intended job. At Neeyamo, we have a dedicated innovation lab that constantly strives to maximize automation in the payroll process. Over the years, experts at Neeyamo have analyzed the payroll cycle deeply and have developed bots to automate various repetitive activities. If you’re a small business that can’t afford to bring on a full-fledged finance team, payroll automation means you can work with a smaller team, which allows you to save money by not paying more employees.
How PureSoftware RPA Delivers Value to the HR / Payroll?

For decades, the payroll function has been the least likely to see automation improvements. A bot can enter the termination in the payroll system and perform the calculations automatically, which could increase final payroll processing accuracy. A payroll administrator can launch the bot when the termination occurs or schedule the bot to periodically search for terminated employees in the company’s human resource information system. Robotic Process Automation, or RPA, is a form of business process automation technology that uses software robots or ‘bots’ to perform routine tasks traditionally done by humans. These bots can be programmed to follow rules-based procedures, and they interact with digital systems in the same way a human user would. Robotic accounting involves the use of Robotic Process Automation (RPA) to streamline and automate accounting tasks like data entry, reconciliation, report generation, and financial analysis.
- The analytical and communication skills used in this process are – and will continue to be – valuable, providing a ‘human’ touch in a world of increasing automation and robotics.
- RPA in HR and payroll processing are new innovations; however, the adoption of RPA for payroll processing is moving forward rapidly.
- It also includes 3% cash back on transit, including taxis/rideshare, parking, trains, and buses.
- Bots can easily scale up or down to meet this demand, without any compromise on speed or accuracy.
- While this kind of smart technology is becoming increasingly common, many smaller local payroll vendors do not have the means to implement it.
Examples of how robotic accounting can be used in accounting processes
- What if there was a way to automate data collection processes by integrating your data sources with your payroll approval processes?
- Payroll functions that RPA bots could assist with or take over include expense payment processing and validating payroll results.
- Timely and accurate payrolls improve employee satisfaction and trust in the organization.
- The American Express Business Gold Card is a premium credit card tailored for LLCs and businesses that prioritize earning rewards in their high-spend categories.
- At Neeyamo, we have a dedicated innovation lab that constantly strives to maximize automation in the payroll process.
- He started his career as a management consultant at The Boston Consulting Group and holds an MBA from Stanford University.
The lack of interoperability within the organization that diminishes the efficiency of the payroll functions can be eliminated. Robotic Process Automation doesn’t mean you have to change the way you operate entirely. Pilot small automation projects first and then build on them and implement on a wider-scale. You’ll need buy-in from other departments across the business including, the C-suite. To gain their approvals, you need to understand what RPA will mean for your business, what processes would benefit from being automated and where RPA will add the most value.
Bonus calculation and processing
Automating payroll reduces operational costs, allowing organizations to invest more in strategic initiatives and achieve significant cost savings. For example, the system would recognize that the number of standard shift hours submitted in the system increased from one month to the next by 10% and would check that the standard shift payout showed a similar increase. The system can also check that the implied tax and social security rates fall within the expected range.
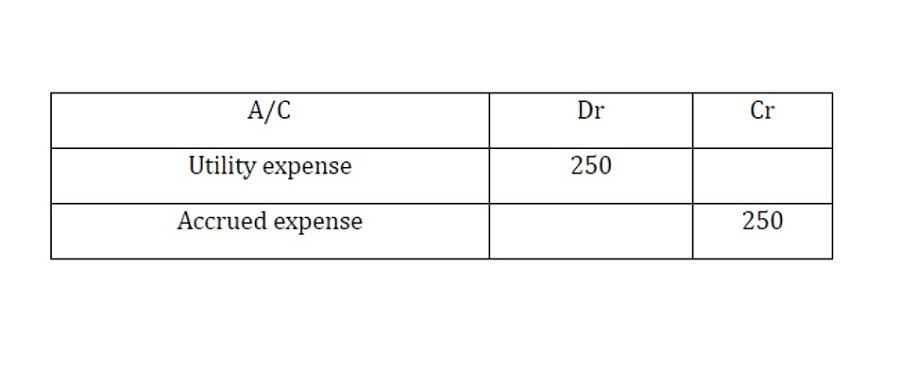
Payroll Processing Improvement is Overdue
This requires human intervention and monitoring to ensure the bot operates smoothly. This means that tasks can be performed outside of traditional working hours, ensuring smooth operations and faster turnaround times. Your staff would no longer be bogged down by mundane and repetitive tasks, which means they can focus on more significant, value-adding tasks. For example, a bot performing bank reconciliation will not miss any discrepancies between the bank statement and the company’s records, ensuring financial accuracy.
Payroll automation software examples
The combination of RPA and Artificial Intelligence (AI) is called CRPA (Cognitive Robotic Process Automation) or IPA (Intelligent Process Automation) and has led to the next generation of RPA bots. It has been transforming the banking industry by making the core financial operations exponentially more efficient and allowing banks to tailor services to customers while at the same time improving safety and security. Although intelligent automation is enabling banks to redefine how they work, it has also raised challenges regarding protection of both consumer interests and the stability of the financial system. This article presents a case study on Deutsche Bank’s successful implementation of intelligent automation and also discusses the ethical responsibilities and challenges related to automation and employment. We demonstrate how Deutsche Bank successfully automated Adverse Media Screening (AMS), accelerating compliance, increasing adverse media search coverage and drastically reducing false positives. This research contributes to the academic literature on the topic of banking intelligent automation and provides insight into implementation and development.
- Real-world examples illustrate the transformative impact of CMS IT Services’ payroll automation solutions.
- As a virtual workforce, this software application has proven valuable to organizations looking to automate repetitive, low-added-value work.
- So, in many ways, this is a great example of robotic process automation (RPI)/artificial intelligence (AI) assuming time-consuming tasks formerly in the domain of payroll employees.
- The card has a points-based rewards system with different points per purchase category.
- By identifying where there are significant outliers, you can increase confidence levels and reduce frustrating and time-consuming manual spot checks.
- QuickBooks Payroll, offered by Intuit, is another popular payroll automation solution, widely recognized for its versatility and integration with the broader QuickBooks accounting ecosystem.
Global Pay-Check

A bot can carry out various reconciliation steps, including checking the payroll register, checking pay rates, checking time worked and absences, and validating deductions. A bot can potentially cut down on errors, which reduces the likelihood of an IRS fine for https://www.bookstime.com/ submitting incorrect reporting. Some companies don’t use a compensation planning tool, and some compensation planning tools don’t integrate with particular variable pay programs. Arttha, from PureSoftware, is a globally trusted financial technology platform.
He started his career as a management consultant at The Boston Consulting Group and holds an MBA from Stanford University. Fiedler is a leading voice on the emerging paradigm of open-source global payroll solutions and the merits of a consolidated global payroll reporting framework. By deploying RPA in payroll globally the data processing can be centralized, standardized, and fully automated. This creates an opportunity to analyze the Big Data generated that comes from all global operations.
- By automating answers to frequently asked questions, RPA can alleviate the burden on payroll staff and provide prompt assistance to your employees.
- By incorporating RPA into payroll automation, companies can improve accuracy, ensure compliance, and enhance the overall payroll management process.
- Pilot small automation projects first and then build on them and implement on a wider-scale.
- This kind of automation is prohibitively expensive for customers to develop on their own.
- It’s an enhanced version of the Spark Miles Select, providing greater rewards in exchange for an annual fee.
We monitor, tune and optimize the RPA execution continuously and manage RPA infrastructure as well. Therefore, it’s essential to communicate the benefits of RPA clearly to the payroll automation staff and provide adequate training and support to ensure smooth adoption. Moreover, if a bot is not programmed correctly, it might accidentally violate data privacy laws.
CONTACT INFO
- Address : BackYard Miracles, Clarkson, WA Australia
- Phone : +61 408927884
- E-mail : [email protected]
- Website : backyardmiracles.com.au
DEVELOPED BY FUTURISTIC WEB MEDIA | Sitemap
